In today's digital age, data management has become a crucial
aspect of using computers and electronic devices efficiently. As technology
evolves, the need for well-organized and optimized storage solutions is more
important than ever. This article will delve into the world of disk management
in operating systems, exploring its significance, tools, and techniques to help
you achieve better performance, data protection, and customization for your
storage devices.
What is Disk Management?
At its core, disk management is the process of organizing
and maintaining data on a storage device, such as a hard disk drive (HDD),
solid-state drive (SSD), optical disk drive (ODD), or flash drive. These
storage devices can store various types of data, ranging from programs and
documents to images, videos, and music. However, for the data to be accessible
and manageable by both the operating system and the user, the storage device
must be divided into smaller units called partitions or volumes. Each partition
or volume can have its own file system, which dictates how data is stored and
retrieved on the device.
The Importance of Disk Management
Efficient disk management is essential for several reasons:
1. Optimize Performance and Efficiency
By allocating the appropriate amount of space for each
partition or volume according to your needs, you can optimize the performance
and efficiency of your storage device. This prevents unnecessary wastage of
space and ensures that each partition operates at its best.
2. Protect Your Data
Disk management allows you to create backups or copies of
your partitions or volumes on another storage device or an online service. This
step is crucial for data protection, safeguarding your valuable information in
case of hardware failures or unexpected events.
3. Troubleshoot Problems
When issues or errors arise on your storage device, disk
management tools enable you to repair or restore damaged partitions or volumes.
This capability can save you from data loss and system malfunctions.
4. Customize Your Storage
Disk management empowers you to tailor your storage device
according to your preferences. You can change the file system, drive letter, or
mount point of your partitions or volumes to suit your specific needs and
workflow.
Accessing Disk Management Tools
The method of accessing disk management tools varies
depending on the operating system you are using. Let's explore how to access
these tools in both Windows and Linux environments.
Disk Management in Windows
Windows offers a user-friendly graphical user interface
(GUI) tool called Disk Management, allowing you to view and manage disk-based
hardware recognized by the operating system. Here's how to access it:
Windows 11 or Windows 10:
Right-click (or long-press) the Start button and select Disk
Management.
Alternatively, you can type diskmgmt.msc in the search box
on the taskbar and press Enter.
Windows 8 or Windows 7:
Press Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
Type diskmgmt.msc and press Enter.
Alternatively, you can go to Control Panel > System and
Security > Administrative Tools and double-click Disk Management.
Disk Management in Linux
Linux provides various command-line tools for disk
management, giving you extensive control over disk partition tables and file
systems. Some of the common tools are:
fdisk: A powerful tool for creating and modifying disk
partition tables, supporting multiple partition table formats such as MBR and
GPT.
parted: A modern tool for managing hard disk partitions,
supporting various file systems and the ability to resize partitions without
data loss.
gparted: A graphical user interface (GUI) tool based on
parted, offering a user-friendly approach to disk management tasks.
mkfs: A tool for creating file systems on partitions,
supporting various file system formats like ext4, NTFS, FAT32, etc.
mount: A tool for mounting partitions or volumes on
directories, allowing access to stored data by assigning a name or location in
the file system hierarchy.
To use these tools in Linux, open a terminal window and type
the commands with appropriate options and arguments. Make sure to have root
privileges or use sudo to execute these commands effectively.
How to Partition a Drive
Partitioning a drive involves dividing a storage device into
one or more logical areas, known as partitions or volumes, for storing
different types of data. This process aids in organizing your data, optimizing
disk space, and improving system performance. Let's explore how to partition a
drive using Disk Management in Windows and gparted in Linux.
Partition a Drive in Windows
To partition a drive in Windows using Disk Management,
follow these steps:
1. Open Disk Management and locate the drive you want to
partition. It should have a label like Disk 0, Disk 1, etc.
2. Initialize the drive if it's new or has no partitions.
Right-click the drive, select Initialize Disk, choose either MBR or GPT as the
partition style, and click OK.
3. Create a new partition from unallocated space, if
available. Right-click the unallocated space, select New Simple Volume, and
follow the wizard to specify size, drive letter, file system, and volume label.
Click Finish to create the partition.
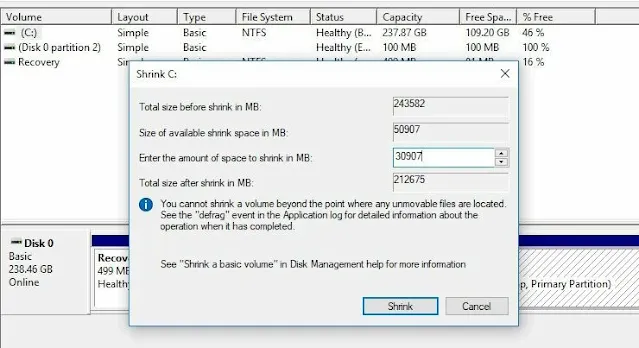
4. Resize or delete existing partitions if needed. Right-click
the partition to modify and select one of the following options:
Shrink Volume: Reduce the partition size to create
unallocated space for a new partition.
Extend Volume: Increase the partition size using adjacent
unallocated space.
Delete Volume: Delete the partition, creating unallocated
space for a new partition.
Partition a Drive in Linux
To partition a drive in Linux using gparted, follow these
steps:
1. Open gparted and select the drive you want to partition
from the drop-down menu at the top right corner. It should have a name like
/dev/sda, /dev/sdb, etc.
2. Create a partition table if the drive is new or has no
partitions. Click Device > Create Partition Table, choose either msdos or
gpt as the partition table type, and click Apply.
3. Create a new partition from unallocated space, if
available. Right-click the unallocated space, select New, and specify size,
file system, and label for the new partition. Click Add to create the
partition.
4. Resize or delete existing partitions if needed.
Right-click the partition to modify and select one of the following options:
Resize/Move: Adjust the partition size and position by
dragging the edges or entering values manually.
Delete: Remove the partition, creating unallocated space for
a new partition.
Once all changes are made, click Edit > Apply All
Operations to implement them on the disk.